What is ECG / EKG (Electrocardiogram)
A simplified explanation


Standard US shipping included (We ship internationally daily)
Product Description
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive test that records and displays the electrical activities produced by heart muscle during a cardiac cycle. The ECG test is a standard clinical tool for diagnosing abnormal heart rhythms and to assess the general condition of a heart, such as myocardial infarctions, atrial enlargements, ventricular hypertrophies, and bundle branch blocks.
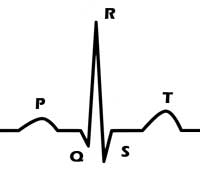
Each EKG cycle consists of 5 waves called PQRST. The P wave represents the normal atrial depolarization; the QRS complex (one single heart beat) corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles; the T wave represents the re-polarization (or recovery) of the ventricles.
A complete ECG is taken using 10 electrodes capturing 12 leads (signals) to get a total picture of the heart. Each lead looks at the electrical activities from a different angle. 12 leads are required for accurate diagnosis purpose; however one lead can offer important information for quick and initial assessment of the patient.
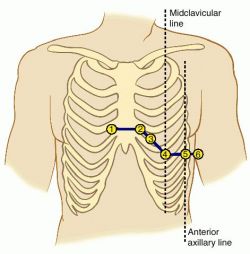
The 10 electrodes consist of 4 bipolar electrodes and 6 unipolar electrodes. The 4 bipolar electrodes are placed on the right arm (RA), left arm (LA), right leg (RL) and left leg (LL). The 6 unipolar electrodes (v1, v2, v3, v4, v5 and v6) are placed on the chest. Together they form 12 leads to get a 3-dimensional picture of the electrical activities. The 12 leads are:
- Lead I: Right arm to left arm
- Lead II: Right arm to left leg
- Lead III: Left arm to left leg
- Lead aVr: Left arm and left leg to right arm
- Lead aVl: Left leg and right arm to left arm
- Lead aVf: Left arm and right arm to left leg
- Lead V1 to neutral
- Lead V2 to neutral
- Lead V3 to neutral
- Lead V4 to neutral
- Lead V5 to neutral
- Lead V6 to neutral
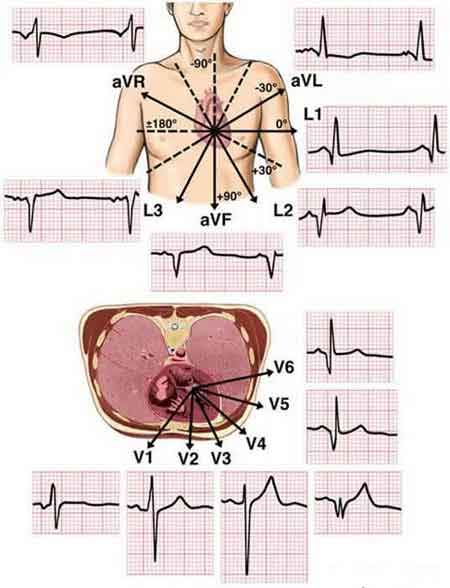
The "a" in the above labels stands for "augmented" as the signals are weaker than other leads and signal amplification is required. The augmented leads use two electrodes to form a negative pole and one for the positive pole. V1 - V6 are measured against an area of zero potential. The following diagram from a blog on www.malaysianbiomed.org gives an excellent depiction of how these 12 leads together capture the electrical activities of the heart and give a 3-dimensional view of the signals.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive test that records and displays the electrical activities produced by heart muscle during a cardiac cycle. The ECG test is a standard clinical tool for diagnosing abnormal heart rhythms and to assess the general condition of a heart, such as myocardial infarctions, atrial enlargements, ventricular hypertrophies, and bundle branch blocks.

Each EKG cycle consists of 5 waves called PQRST. The P wave represents the normal atrial depolarization; the QRS complex (one single heart beat) corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles; the T wave represents the re-polarization (or recovery) of the ventricles.
A complete ECG is taken using 10 electrodes capturing 12 leads (signals) to get a total picture of the heart. Each lead looks at the electrical activities from a different angle. 12 leads are required for accurate diagnosis purpose; however one lead can offer important information for quick and initial assessment of the patient.
The 10 electrodes consist of 4 bipolar electrodes and 6 unipolar electrodes. The 4 bipolar electrodes are placed on the right arm (RA), left arm (LA), right leg (RL) and left leg (LL). The 6 unipolar electrodes (v1, v2, v3, v4, v5 and v6) are placed on the chest. Together they form 12 leads to get a 3-dimensional picture of the electrical activities. The 12 leads are:

- Lead I: Right arm to left arm
- Lead II: Right arm to left leg
- Lead III: Left arm to left leg
- Lead aVr: Left arm and left leg to right arm
- Lead aVl: Left leg and right arm to left arm
- Lead aVf: Left arm and right arm to left leg
- Lead V1 to neutral
- Lead V2 to neutral
- Lead V3 to neutral
- Lead V4 to neutral
- Lead V5 to neutral
- Lead V6 to neutral
The "a" in the above labels stands for "augmented" as the signals are weaker than other leads and signal amplification is required. The augmented leads use two electrodes to form a negative pole and one for the positive pole. V1 - V6 are measured against an area of zero potential. The following diagram from a blog on www.malaysianbiomed.org gives an excellent depiction of how these 12 leads together capture the electrical activities of the heart and give a 3-dimensional view of the signals.

Shipping Information
Shipping Weight: 0.00 Pounds
Availability: In stock! Ready to ship.
Shipping Cost: US Shipping included! Int'l Shipping calculated at checkout
In-stock items are normally shipped within 24-48 hours on business days. For special handling or overnight shipping, please call us at 281-664-1209.
Manufacturer Information
Manufacturer:
Item Code:
Product belongs to these categories...
Home ECG / EKG Monitor

